Deep-sea fish living in the depths of the ocean undergo harsh conditions. They are exposed to high pressure, sudden temperature changes, and an environment without sunlight. The deepest-sea fish species have unusual and frightening appearances. They are monsters from the deep, from the harsh environment due to the lack of light and high pressure. Despite the mentioned conditions, some fish species have adapted to life in the deep sea environment.
Let’s find out the top nine deepest-sea fish species in this article.
Features of the deepest sea fish.
The fish that live in the depths of the ocean, where conditions are harsh – completely dark and high pressure, often have unique characteristics such as:
- Reduced bones
- Reduced muscle mass
- Limited mobility
- Large jaws
- Enormous stomachs
- Slow metabolic rates
- Bioluminescence and more.
The top deepest sea fish species.
Please refer to the list of the deepest sea fish species suggested below:
1. Viperfish (Chauliodus sloani)
Viperfish belongs to the Stomiidae family. It lives at depths of 200-4700 meters. Viperfish can be recognized by their long and sharp teeth that clearly do not fit inside their mouth.
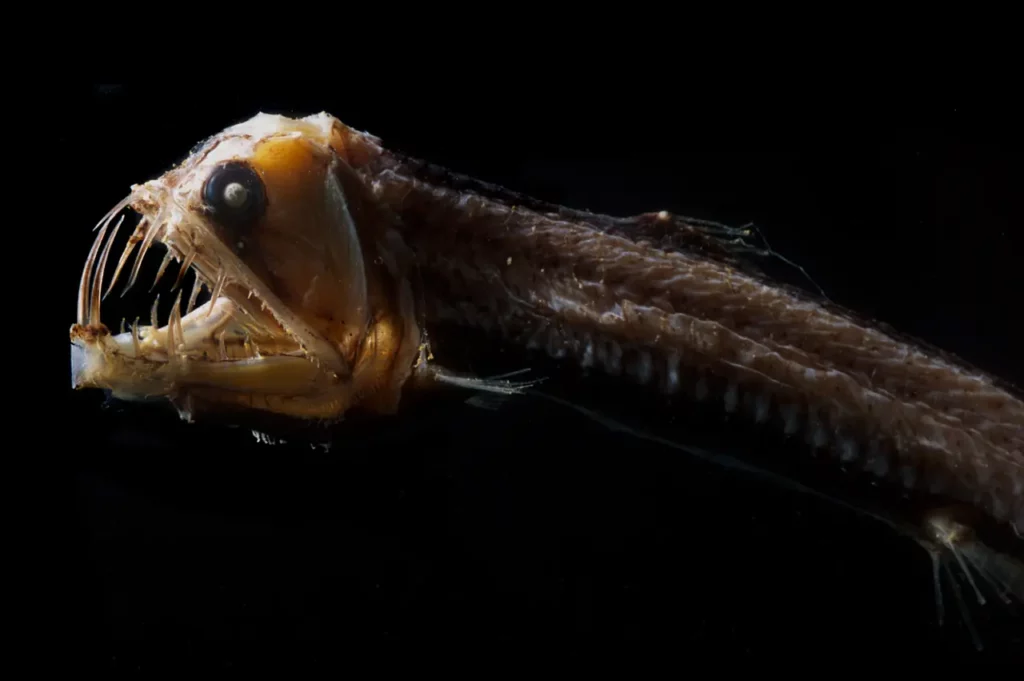

The body of this fish is elongated, silver in color and emits light. They can grow up to 35 cm tall. They live in warm regions between the Atlantic Ocean, northern Indian Ocean and eastern Pacific Ocean, north of the equator.
2. Fangtooth fish
The Fangtooth fish is a deep sea predator with extraordinary adaptations for hunting. It has large, flexible jaws and sharp teeth for capturing prey. Its body also has light-producing organs and bioluminescent cells.

3. Pacific Blackdragon
The Pacific Blackdragon is also among the top nine deepest living fish in the ocean. They have a black body resembling a snake and large teeth. The females are four times longer than males. The Pacific Blackdragon attracts prey with a light-emitting organ at the end of a whisker-like appendage that extends beyond its lower jaw. It has light-producing organs running along its belly.
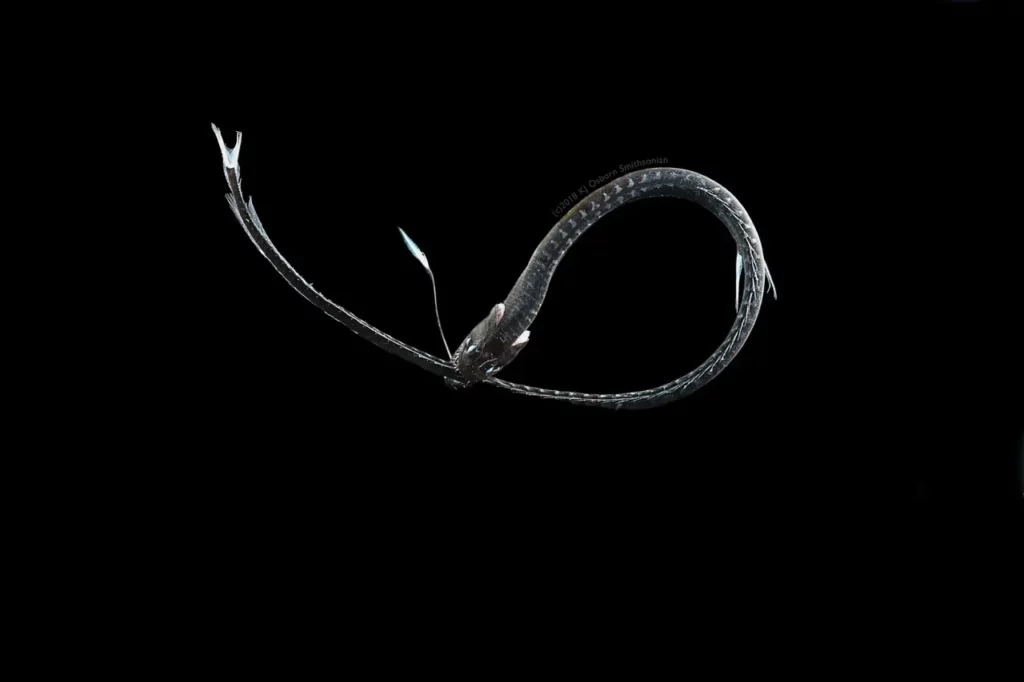
4. Tripod spider fish
The tripod spider fish rises from the deep ocean floor on a tripod-like structure formed by elongated ventral and tail fins. Its main food source is shrimp. The fish has small eyes and a large opening for a mouth.
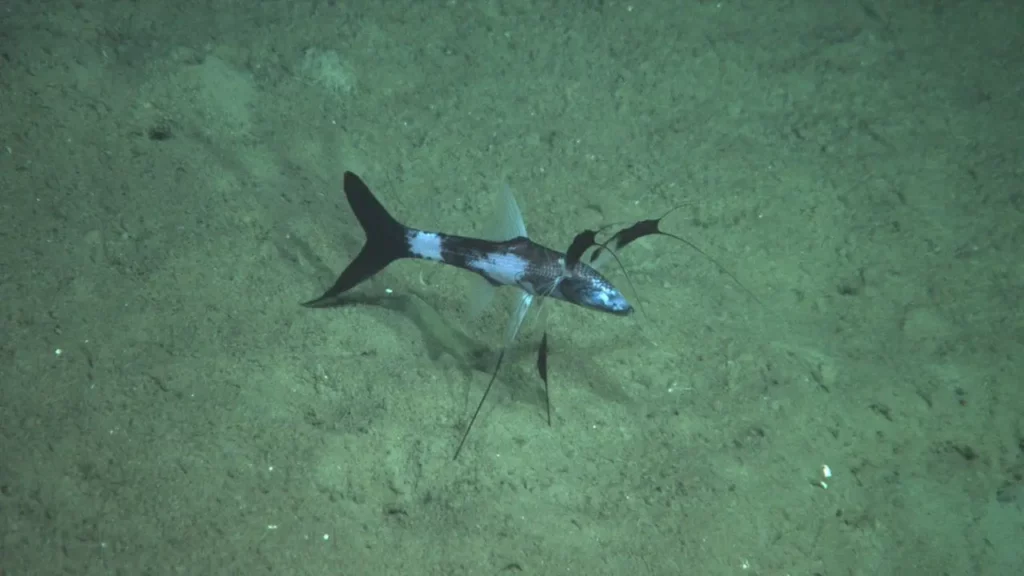

5. Anglerfish
Species of deep-sea fish belongs to the family Myctophidae, lanternfishes. It is one of the important links in the ocean food chain, feeding on planktonic shrimp.

6. The black ruff
The black ruff is a deep-sea fish that lives solitary or in small groups. Its body is cylindrical and flattened on the sides, black on the back and gray on the belly. The size of this fish can grow up to 150 cm.
Although the black ruff lives in the deep sea, it also ventures into shallower waters. Juveniles have dark horizontal stripes on both sides and live near the surface. They reproduce during the fall and winter seasons.
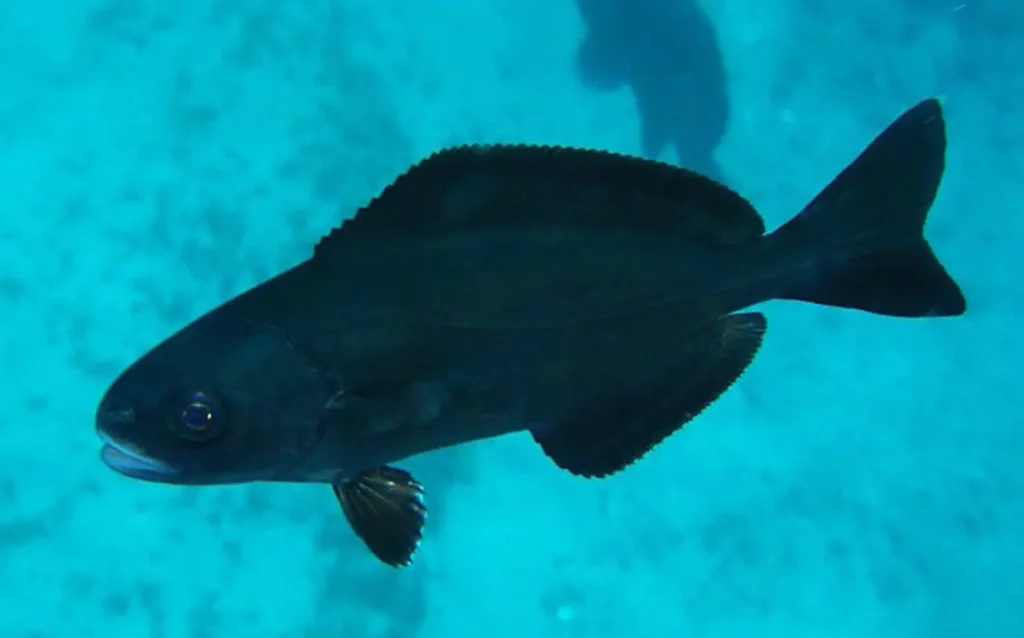

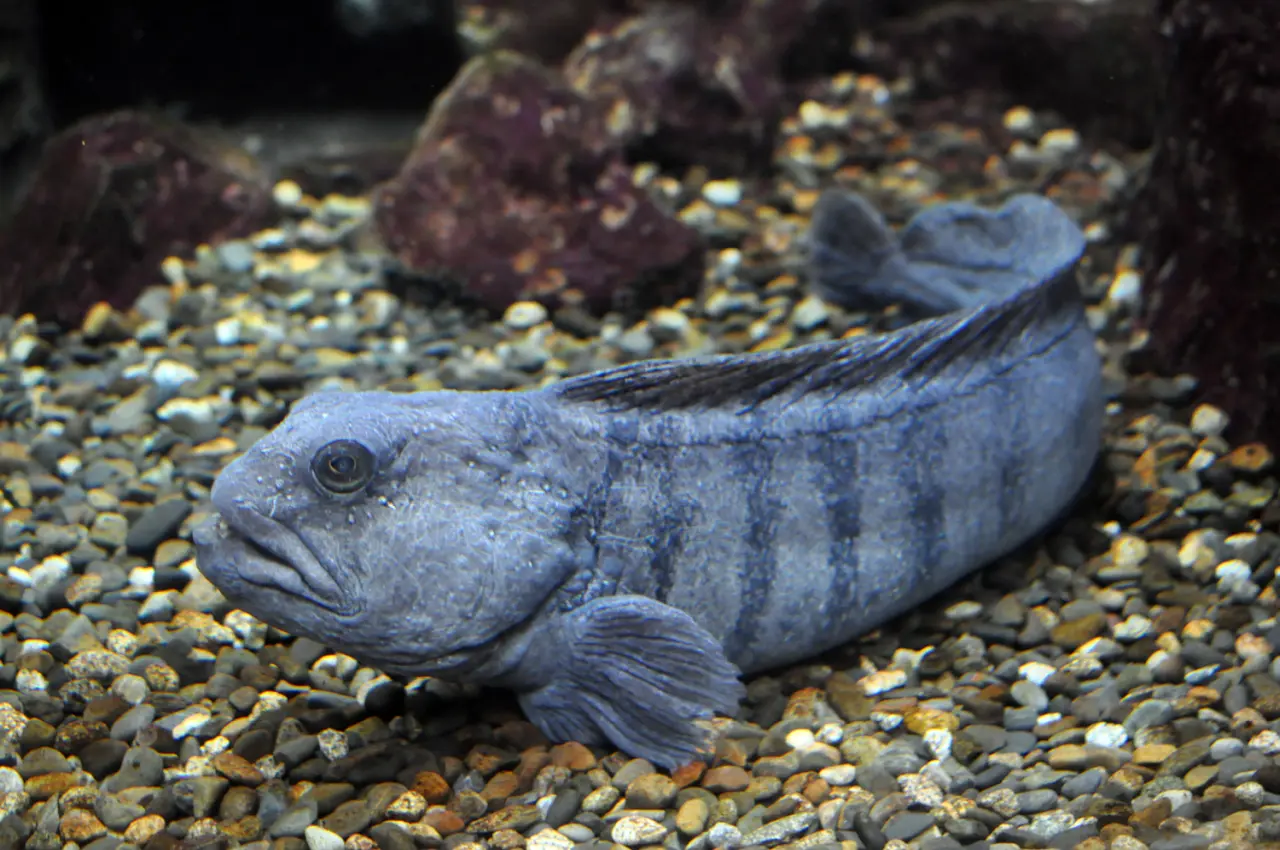
7. Atlantic wolffish
The Atlantic wolffish belongs to the family Anarhichadidae and lives at depths of up to 500 meters below the ocean floor. This type of fish primarily uses its strong jaws to eat shellfish, spiny-skinned animals, and crustaceans.

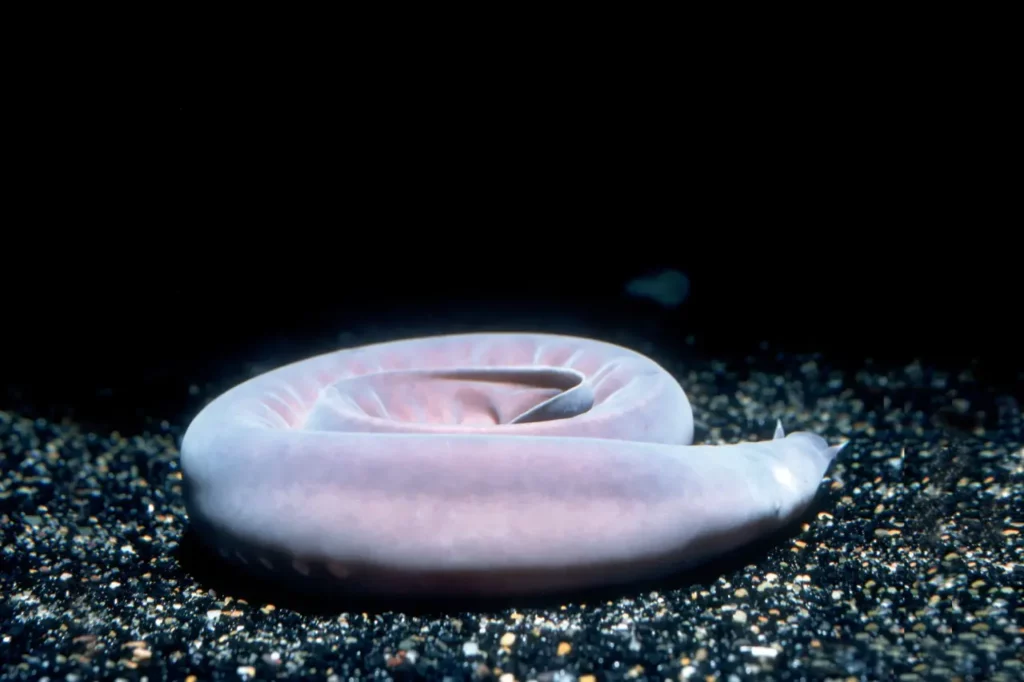
8. Pacific Hagfish
Pacific Hagfish, or the slime eel, is also one of the deep-sea fish living at great depths below the ocean floor. This species is found at a depth of 914 meters below the ocean floor in the Pacific region. The average body size of the Pacific Hagfish is around 63cm. Their food usually consists of dead or dying fish, as they enter the body and eat the internal organs.

9. Gulper Eel
Gulper eel, also known as pelican eel or umbrella-mouth gulper, is a species of eel that lives at depths of around 1,200 meters below sea level. Its favorite food is small crustaceans.
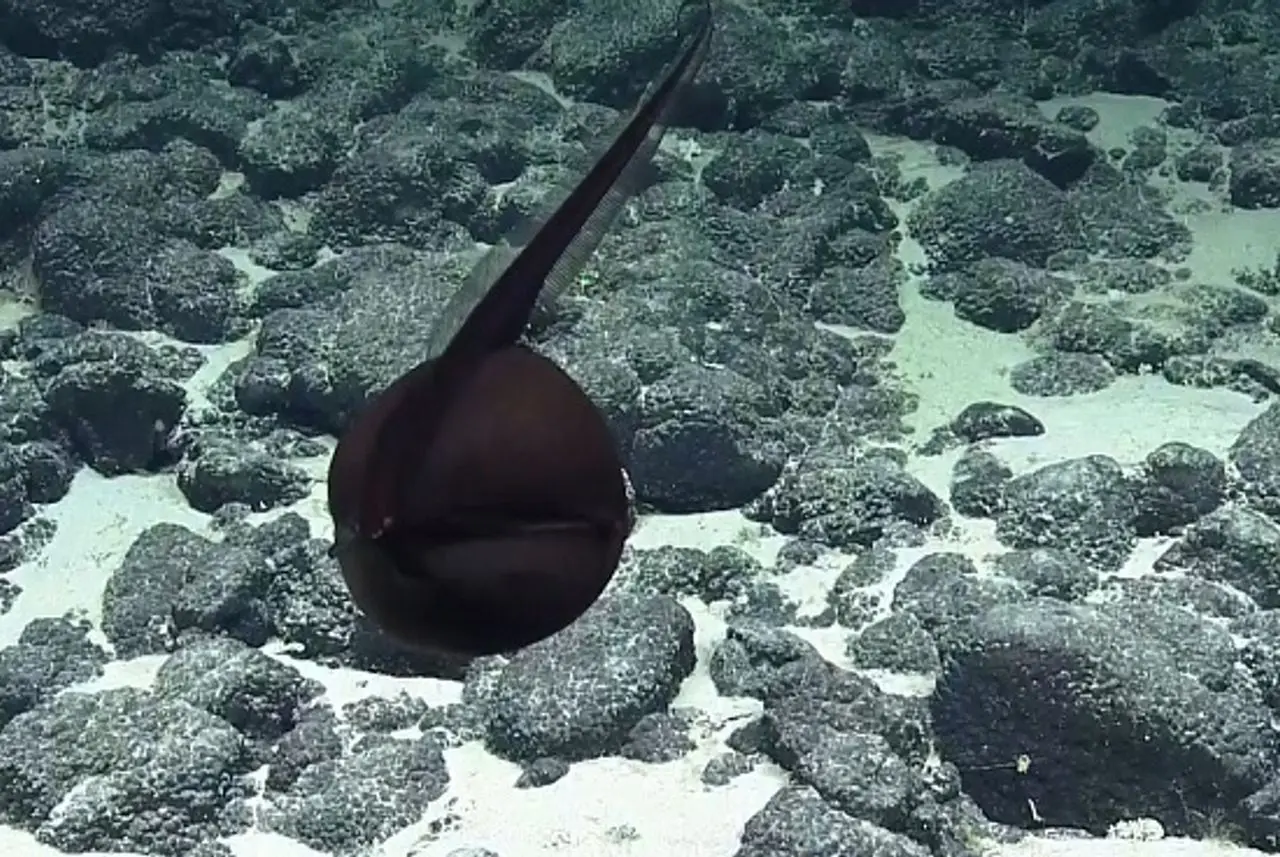

The stomach of this fish species has the ability to expand flexibly to contain more food.
Above are the nine most endangered fish species in the world, however, they can exist with us longer if we join hands to protect for a beautiful planet.








